GASTRULATION
GASTRULATION
gastrula,
from the Greek word gaster, ..meaning stomach The 2nd major phase of embryonic dvtThe
embryo is transformed from hollow ball of cells (the blastula) into a 3-layered
stage Gastrula A
dramatic re-arrangement of the cells of the blastula Cells
are given new positions and new neighbours, and the multilayered body plan of
the organism is established At this stage,cells that will form the endodermal and mesodermal organs are brought inside the
embryo, whilethe cells that will form the skin
and nervous system are spread over its outside surface.3 germ layers
–outer ectoderm, inner endoderm, and interstitial mesoderm—are first produced during gastrulation The movements of gastrulation
involve the entire embryo.
Cell migrations in one part of the
gastrulating embryo must be intimately coordinated with other movements
occurring simultaneously The
patterns of gastrulation
vary enormously throughout the animal kingdom…….but there are basic types of cell movements The gastrulation
of any particular
organism is a collection of several
of the following cell
movements
Types
of cell movements during gastrulation
Gastrulation usually involves some combination of
these types of movements
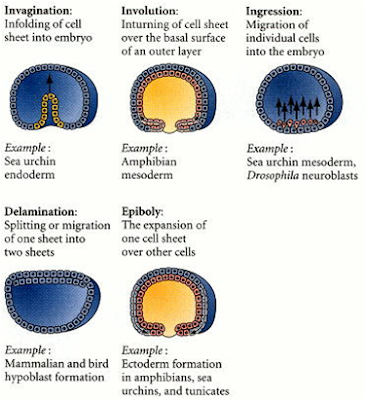
Invagination: The infolding of a
region of cells, much like the indenting of a soft rubber ball when it is
poked. (cell movt) Involution: The inturning or
inward movement of an expanding outer layer so that it spreads over the
internal surface of the remaining external cells. (cell movt) Ingression: The migration of
individual cells from the surface layer into the interior of the embryo. (cell movt)•Delamination: The splitting of one cellular sheet into two
more or less parallel sheets. Epiboly: The
movement of epithelial sheets (usually of ectodermal cells) that spread as a unit, rather than
individually, to enclose the deeper layers of the embryo. (cell
movt) Gastrulation
process will result into formation of a three-layered
embryo with a primitive
gut (the
archenteron)The three cell layers will later develop into
all the parts of the adult animal.………. How does a cell know what it is supposed
to grow up?
•Induction is the process during
which individual cells are "told" what they are supposed to
become. Spemann
and his graduate student Hilde Mangold (1898–1924) demonstrated that specific cells
of the blastopore are
the only determining region.Further
experimentation demonstrated that during gastrulation cells became committed to their
developmental fates.
GASTRULATION in Sea
Urchin
The late sea urchin blastula consists of a
single layer of about 1000 cells that form a hollow ball, somewhat flattened at
the vegetal end.The process of gastrulation in sea urchin develops to the pluteus larva stage
The process of gastrulation in sea urchin.
A. Ingression of primary mesenchyme
;Thickenning
& flattlenning of the vegital pole to form a vegital plate (vp) Cells at the centre of the vp beginns to extend & contract long by
the process called filopodia;The cells dissociate to form the epithelial monolayer These cells, derived from the micromeres, are called the primary mesenchyme (pm) The ingression of the micromere descendants into the blastocoel is caused by these cells losing
their affinity for their neighbours and for the hyaline membrane and acquiring
a strong affinity for a group of proteins that line the blastocoel
B. First
stage of archenteron invagination
;Cells remain after the pm has left undergoes
some important changes.They remain bound to one another
and to the hyaline layer of the eggs They move to fill the gaps caused
by the ingression of the pm.The vegetal plate bends inward
and invaginates into the blastocoel to form the archenteron & the opening called blastopore
C. Second and third stages of archenteron invagination
The 2nd phase of archenteron formation begins after a brief pause from
the 1st
stage,The archenteron extends dramatically, sometimes tripling its
length.The wide, short gut rudiment is transformed into a long, thin
tube;Here the cells of the archenteron rearrange themselves by
migrating over one another and by flattening themselves. This phenomena is
known as convergent
extension. (cell movt) Moreover, cell division continues, producing more endodermal and secondary mesenchyme cells as the archenteron extends
Cell rearrangement during the extension
of the archenteron in sea urchin embryos
The archenteron has a circumference 6 to 8 cells.
2nd & 3rd
stage……cont’d
The
last phase is initiated by the tension provided by secondary mesenchyme
cells, which form at the tip of the archenteron,Filopodia are
extended from these cells through the blastocoel
fluid to contact the inner surface of the blastocoel
wall,The filopodia attach to the wall at the
junctions between the blastoderm cells and then shorten, pulling
up the archenteron.As the top of the archenteron meets the blastocoel wall in the target region, the
secondary mesenchyme cells disperse into the blastocoel, where they proliferate to form
the mesodermal organs
Where the archenteron contacts the wall, a mouth is eventually
formed
GASTRULATION in Frogs
At
specific region below the equator the blastoderm cells assume an elongated bottle like shape.They
move toward the interior of the blastula. As the cells move further inside, an invagination
happens.A
deepening of invagination
results in a cavity called archenteron or gastrocoel.The
opening of the archenteron on the surface of blastula is called blastopore.The region dorsal to the blastoporal
opening is called dorsal
lip and on the ventral edge is a ventral lip.The surface cells representing several
prospective zones of the embryo begin to wander inside through the blastopore.These inwandering of cells is termed as involution.
While
the exterior mesodermal cell
involute
inside, their place is taken up by the ectodermal cells.The
expansion of the ectoderm is due to epiboly.The blastopore is
gradually covered by certain endodermal cells. The closing cells of the blastopore
constitute the yolky
plug. Gradually the yolky plug withdraws to the
interior and the blastopore gets reduced into a narrow slit.
GASTRULATION in Frogs
REFERENCES
Gilbert,S.F(2013).Develepmental
Biology,Sanderland Mass,Sineaur Association Inc
Slack,J.M.W(2013).Essential
Develepmental Biology OXFORD, Willey-Blackwell
Wolpert.l and Tickle.c
(2011),Principles of Develepmental Oxford and New York University Press





No comments: