DIFFERENTIATION OF NEURAL TUBE
DIFFERENTIATION OF NEURAL TUBE
;
Neural tube; this is the embryos precusor to the central nervous system which
comprises the brain and spinal cord.The differentiation of the neural tube into various regions of the central nervous system occurs in three different ways 1.On the gross anatomical level,the neural tube and its lumen bulge and constrict to form chambers of brain and the spinal cord.2;At the tissue level; the cell population within the wall of the neural tube rearrange them selves to form different function regions of the brain and spinal cord .3;On the cellular level; neuroepithelial cells themselves differentiate into numerous types of nerve cell (neurons) and supportive cell (glia).Early development of most vertebrate brain is similar but because of human brain may be the most organized piece of matter in the solar system, Is the most interesting organ in the animal kingdom, this development supposed to make Homo sapient.
THE ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR AXISThe anterior portion undergoes drastic changes and the neural tube balloons to form three primary vesicles; Those are1Prosencephalon (forebrain)2Mesencephalon(midbrain)
3Rhombosencephalon(hindbrain); The posterior end of the neural tube closes and the secondary vesicles bulge to form href="http://www.chempapy.blogspot.com/">optic vesicles. These optic vesicles extend laterally from each side of the developing forebrain;The tree primary brain vesicles are subdivided as development continues such that;
Prosencephalon become sub divided into the anterior telencephalon and dincephalon.
.
,
,,
;
VENTRAL PATTERNING OF THE NEURAL TUBEThe specification of the ventral neural tube appears to be mediated by external tissues.One agent of ventral specification is the sonic hedgehog protein probably orignating from the notochord.Another agent specifying the ventral neural cell type is retinoid acid which probably comes from adjacent somites.Sonic hedgehog establishes a gradient, and different levels of this protein cause the formation of different cell types.In the notochord sonic hedgehog is processed by cholestol-mediated cleavage and active form of protein(the amino-terminal portion) which is secreted from the notochord.The secreted sonic hedgehog induce the medial hinge cells to become the floor plate of the neural tube, these floor plate cells also secrete sonic hedgehog which forms a gradient highest at the most ventral portion of the neural tube.Those cells adjacent to the floor plate that receive high concentration of sonic hedgehog become ventral (v3) neurons; while the next group of cells exposed to slightly less sonic hedgehog become motor neurones. }The next two groups of cells receiving progressively less of this protein become v2 and v1 interneuron's.-The different concentration of sonic hedgehog function by causing the different types of transcription factors. }These transcription factors in activate the genes whose protein products give the cell its identity.Sonic hedgehog may also work by repressing the expression of genes encoding dorsal neural tube transcription factors.These genes would otherwise be expressed throughout the neural tube.
;
VENTRAL PATTERNING OF THE NEURAL TUBEThe specification of the ventral neural tube appears to be mediated by external tissues.One agent of ventral specification is the sonic hedgehog protein probably orignating from the notochord.Another agent specifying the ventral neural cell type is retinoid acid which probably comes from adjacent somites.Sonic hedgehog establishes a gradient, and different levels of this protein cause the formation of different cell types.In the notochord sonic hedgehog is processed by cholestol-mediated cleavage and active form of protein(the amino-terminal portion) which is secreted from the notochord.The secreted sonic hedgehog induce the medial hinge cells to become the floor plate of the neural tube, these floor plate cells also secrete sonic hedgehog which forms a gradient highest at the most ventral portion of the neural tube.Those cells adjacent to the floor plate that receive high concentration of sonic hedgehog become ventral (v3) neurons; while the next group of cells exposed to slightly less sonic hedgehog become motor neurones. }The next two groups of cells receiving progressively less of this protein become v2 and v1 interneuron's.-The different concentration of sonic hedgehog function by causing the different types of transcription factors. }These transcription factors in activate the genes whose protein products give the cell its identity.Sonic hedgehog may also work by repressing the expression of genes encoding dorsal neural tube transcription factors.These genes would otherwise be expressed throughout the neural tube.
.
.
;
,
,
.IMPORTANCE OF SONIC HEDGEHOG
.The importance of sonic hedgehog in
,
.inducing and patterning the ventral
.
,portion of the neural tube can be
,
.shown experimentally, for instance if
.
.notochord fragments are taken from
.
;one embryo and transplanted to the
,lateral side of a host neural tube, the
,host neural tube will form another set
of floor plate cell at its sides.The floor plate cell once induced,
.
induce the formation of motor
.
.neurons on their side. -The same
results can be obtained if notochord
fragments are replaced by pellets of
cultural cell secreting sonic hedgehog
More over, if a piece of notochord is
removed from an embryo, the neural
tube adjacent to the deleted region
will have no floor plate cells.
DORSAL PATTERNING OF THE NEURAL TUBE;The dorsal fate of the neural tubes are
established by proteins of the
TGF is super family especially
the bone morphogenic proteins
four and seven, dorsalin and actins Initially BMP4 and BMP7 are found in epidermis.
Just as the notochord established as secondary signaling centre- the floor plate cells –on the ventral side of the neural tube,
The epidermis establishes a secondary signaling centre by inducing BMP4 expression in the roof plate cells of the neural tube The BMP4 protein from the roof plate induces a cascade of TGF-B superfamily proteins in adjacent cells.
.Different sets of cells are thus exposed to different concentrations of TGF-B superfamily proteins at different times (the most dorsal being exposed to more factors at higher concentrations and at early times) The temporal and concentrations gradients of the TGF-B superfamily proteins induce different types of transcription factors in cells at different distance from the roof plate, there by giving them identities.

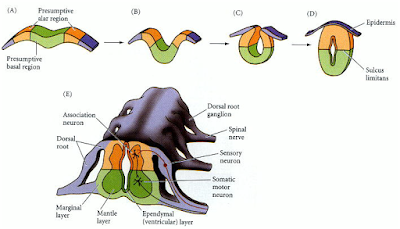
In the spinal cord and medulla;the three zones (ependymal, mantle and marginal) retain through out development. The grey matter (mantle) become butterfly shaped structure surrounded by white matter both in encased in a connective tissue. As the neural tube matures a longitudinal groove the sulcus limitans divide into dorsal and ventral halves. The dorsal portion receives inputs from sensory neurons while the ventral portion is involved in effecting various motor functions

In the spinal cord and medulla;the three zones (ependymal, mantle and marginal) retain through out development. The grey matter (mantle) become butterfly shaped structure surrounded by white matter both in encased in a connective tissue. As the neural tube matures a longitudinal groove the sulcus limitans divide into dorsal and ventral halves. The dorsal portion receives inputs from sensory neurons while the ventral portion is involved in effecting various motor functions
REFERENCES
}RAVEN,P.H(1986) Biology QH 308.2R38, Mosby college publisher united State of America.
}GIBERT S.F (2000) Developmental BIOLOGY 6th Edition Swarthy more college Sunderland,Sinauer Association.




No comments: