Air pollution
AIR POLLUTION
Air pollution is a chemical, physical (e.g. particulate matter), or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphereThere are many substances in the air which may impair the health of plants and animals (including humans), or reduced visibility
These arise both from natural processes and human activity.Substances not naturally found in the air or at greater concentrations or in different locations from usual are referred to as 'pollutants'
Pollutants can be classified as ,Either Primary or Secondary.
Primary pollutants are substances directly produced by a process E.g., Ash from a volcanic eruption orThe carbon monoxide gas (CO) from a motor vehicle exhaust.Secondary pollutants are not emitted
They form in the air when primary pollutants react or interact.An important example of a secondary pollutant is ground level ozone .One of the many secondary pollutants that make up photochemical smog.
Major primary pollutants produced by human activity include:
Sulfur oxides (SOx) especially sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) especially nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gasVolatile organic compounds (VOC), such as hydrocarbon fuel vapors and solvents
Note: some pollutants may be both primary and secondary: that is, they are both emitted directly and formed from other primary pollutants
Sources of air pollution
Anthropogenic sources:Smoke stacks of power plants, manufacturing facilities, municipal waste incinerators.Mobile Sources e.g., Motor vehicles, Aircraft.Controlled burn practices used in agriculture and forestry management.Marine vessels, such as container ships or cruise ships, and related port air pollution.Chemicals, dust and crop waste burning in farming.Fumes from paints, hair sprays, aerosol sprays and other solvents.Waste deposition in landfills, which generate methane.Burning wood, fireplaces, stoves, furnace and incinerators
Natural sources:Dust from natural sources, usually large areas of land with little or no vegetation
Methane, emitted by the digestion of food by animals, for example cattle;Radon gas from radioactive decay within the Earth's crust,Smoke and carbon monoxide from wildfires
Volcanic activity, which produce sulfur, chlorine, and ash particulates.
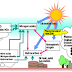
Episode of air pollution during which relatively high levels of ground-level ozone, O3 – an undesirable constituent of air at low altitudes – are produced as a result of the light-induced reaction of pollutants
Is sometimes characterized as “an ozone layer in the wrong place” to contrast it with the stratospheric ozone depletion problems discussed earlier.
The photochemical smog phenomenon was first observed in Los Angeles in the 1940s, and has generally been associated with that city ever since
Ozone is photochemically formed by the interaction between NOx- (Nitrogen oxides) and
VOC's (Volatile Organic Compounds) components.Vital ingredient in photochemical smog is
Sunshine - increases the concentration of free radicals that participate in the chemical process of smog formation.The final products of smog are Ozone,Nitric acid, andPartially oxidized and
In some cases nitrated organic compounds
VOCs + NO2. + Sunlight → Mixture of O3, HNO3, Organics.
The most reactive VOCs in urban air are Hydrocarbons that contain a C=C bond - since they can add free radicals.Other hydrocarbons are also present and can react But the rate of their reaction is slow
Their reaction can become important in late stages of photochemical smog episodes.Nitrogen oxide pollutants gases are produced whenever a fuel is burnt in air with a hot flame,Some of the nitrogen and oxygen gases in air combine to form nitric oxide, NO
N2+ O2 Flame →2NO. (Nitric oxide)
The greater the flame temperature, the more NO. that is produced.The nitric oxide is gradually oxidized to nitrogen dioxide, NO2 over a period of minutes to hours, depending upon the concentration of the pollutant gasesNO2 and NO in air are collectively referred to as NOx.
The small levels of NOx in clean air result in part from:The operation of the above reaction in the very energetic environment of lightning flashes and in part from the release of NOx and NH3 from biological sources,Because the reaction between N2 and O2 has a high activation energy
It is negligibly slow except at the very high temperatures such as occur in the modern combustion engines in vehicles,Particularly when travelling at high speeds – and in power plants.
In order that a city be subject to photochemical smog, several conditions must be fulfilled:
(a) There must be substantial vehicular traffic in order to emit sufficient NOx, hydrocarbons, and other VOCs into the air
(b) There must be warmth and ample sunlight in order for the crucial reactions, e.g. photochemical, to proceed at rapid rate.
(c) There must be relatively little movement of the air mass so that the reactants are not diluted.
(d) Geographical reasons e.g. presence of mountain, valleys
Dense polluted cities such as Los Angeles, Tokyo, Mexico city, Athens and Rome are subject to frequent smog episode.E.g. the air in Mexico City is so polluted by ozone and smog, and by lead from compounds added to gasoline;Responsible for thousands of premature death annually
In the centre of the city residents can purchase pure oxygen from booths to help them breathe more easily.In 1990, Mexico City exceeded the WHO air guideline on 310 days;In 1992, ozone levels reached as high as 400ppb;Athens and Rome, as well as Mexico City, now attempt to limit traffic during smog episodes;Due to long range transport of primary and secondary pollutants in air currents, many areas which themselves generate few emissions are subject to regular episodes of high ground- level ozone and other smog oxidants
E.g., some rural areas which lie in the path of such polluted air masses experience higher levels of ozone than do nearby urban areas, because in the cities some of the ozone is eliminated by reaction with nitric oxide released by cars into the air.An example is the farmland in southwest Ontario, which often receives ozone-laden air from industrial regions in the United States that lie across Lake Erie from it, as a result of the damage caused by this pollution, crops such as white beans can longer be grown successfully in this area,Elevated levels of ozone also affect materials:It hardens rubber - reducing the useful lifespan of consumer products such as automobile tires, and Bleaches colour from some materials such as fabrics.
Eutrophication
Is a process whereby water bodies, such as lakes, estuaries, or slow-moving streams receive excess nutrients that stimulate excessive plant growth (algae, periphyton attached algae, and nuisance plants weeds).This enhanced plant growth, often called an algal bloom. (Blue-green algae called Mycophyceae e.g. Anabaene flos-aquae)
Sources of Nutrients
Eutrophication is a natural process however, humans in their everyday activities can exacerbate the process:Point sources (can locate the causes ,Sewage treatment plant discharges,Storm sewer discharges,Industrial discharges,Non-point sources (can’t locate the cause, it’s everywhere) Atmospheric deposition,Agricultural runoff (fertilizer, soil erosion),Septic systems,Eutrophication: a process by which a body of water progresses from its origin to its extinction. This process happens in stages.Bad taste and odor : some of the algal species that "bloom" produce toxins (geosmin, MIB), water taste and odor deteriorates.Oxygen depletion: penetration of light into the water is diminished. This occurs because the algae forms mats as a result of being produced faster than they are consumed. Diminished light penetration decreases the productivity of plants living in the deeper waters and hence their production of oxygen.Under anoxic conditions iron, manganese, ammonia and phosphorous are released into the water column, anaerobic bacteria flourish, producing hydrogen sulfide.
Effects on water quality
Effects on treatment costs and compliance.Bad taste, odor, and high organics increase operational costs.Compliance with local and international regulations becomes more difficult to achieve.
Effects on recreational activities,Recreation: Lowered oxygen results in the death of fish that need high levels of dissolved oxygen "DO"), such as trout, salmon and other desirable sport fish. The community composition of the water body changes, with fish that can tolerate low DO, such as carp predominating.Changes in fish communities have ramifications for the rest of the aquatic ecosystem like the explosion of mosquitoes.
Effects on biodiversity
Decrease in the diversity of zooplanktons due to death of some which can not tolerate the situation.
Disease to humans e.g. Blue Baby syndrome, which can result to death.Increase of phytoplanktons e.g. algae
Blue Baby Syndrome
Is the illness that occurs when a child drink water containing large amount of nitrates.
The body’s digestive system converts nitrates to nitrites, (using E. coli) changing oxyhemoglobin to metheglobin, which cannot carry oxygen. Mucous membranes turn blue, impairing functions.

No comments: